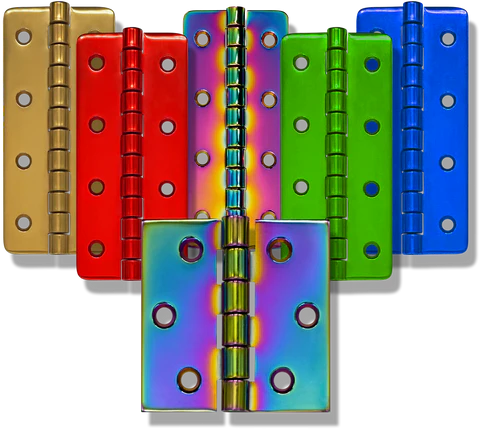
PVD Coating
The Physical Vapor Deposition method is a low temperature vacuum coating method that uses a variety of deposition technologies to generate positively charged, highly energized metal ions, which, when combined with a reactive gas, form highly durable coatings with tailored physical, structural, and tribological properties.

Powder Coating
A powder coating is applied as a free-flowing, dry powder. Electrostatic coatings are applied electrostatically and are typically cured either by heat or ultraviolet light, unlike liquid paints, which are delivered through an evaporating solvent.
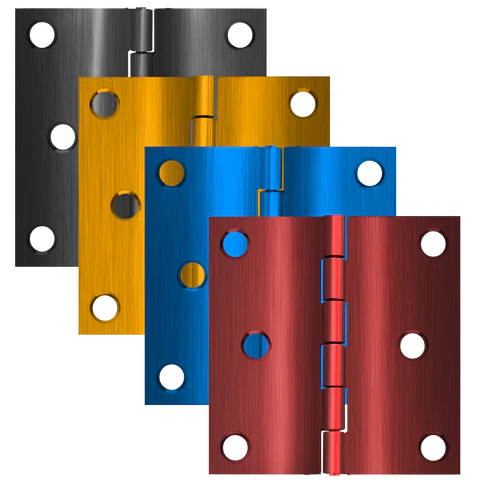
Anodized
As an electrolytic cell's anode electrode, the part being treated is called anodized. In addition to providing better adhesion to paint primers and glues, anodizing increases the resistance of metal to corrosion and wear. The use of anodic films for cosmetic purposes is also possible, either with thick porous coatings that can absorb dyes or thin transparent coatings that add reflected light wave interference effects.
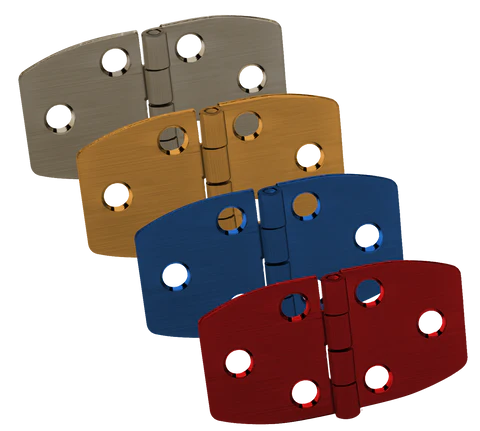
Hard Anodized
As an electrolytic cell's anode electrode, the part being treated is called anodized. In addition to providing better adhesion to paint primers and glues, anodizing increases the resistance of metal to corrosion and wear. The use of anodic films for cosmetic purposes is also possible, either with thick porous coatings that can absorb dyes or thin transparent coatings that add reflected light wave interference effects.

Titanium Nitride (TiN)
Titanium nitride (TiN) coatings are not only wear-resistant but also inert. It increases tool life two to ten times over uncoated tools when used on cutting tools, punches, dies, and injection mold components.

Diamond Like Coating (DLC)
In the commercial industry, Diamond Like Carbon (DLC) coatings have been widely successful as a result of PVD + PECVD technology. Calico's carbon-based coating has extreme hardness due to the diamond crystal structure and is soft and lubricious due to the graphite crystal structure. By combining these two structures, the coefficient of friction is reduced by 200%-500% compared to traditional tribological PVD coatings. As DLC coatings are generally amorphous (without typical crystal structure), they can be deposited with elements such as hydrogen and metals such as chromium. The properties and structures of DLC coatings are significantly influenced by these integral components and techniques.
The properties of DLC coatings in terms of increased hardness, coefficient of friction, roughness, adhesion level, load carrying capacity, resistance to humidity influenced degradation, fatigue tolerance, etc. A variety of deposition parameters, deposition technology, and combinations of materials can be used to customize a DLC coating. Calico's Diamond Like Carbon (DLC) coatings contain significant SP3 bonds in a dense, metastable form of hydrogenated amorphous carbon (a-C:H)














